Introduction
Machine learning models enabled by artificial intelligence (later referred as AI) complement the work of designers by efficiently analyzing vast amounts of quantitative data. Based on data collected from customers, AI is able to create various alternative hypothesis on what kind of impact design can achieve. By modeling customer behavior machine learning models can predict which combinations of various possible qualities have the greatest potential for improving customer experience.
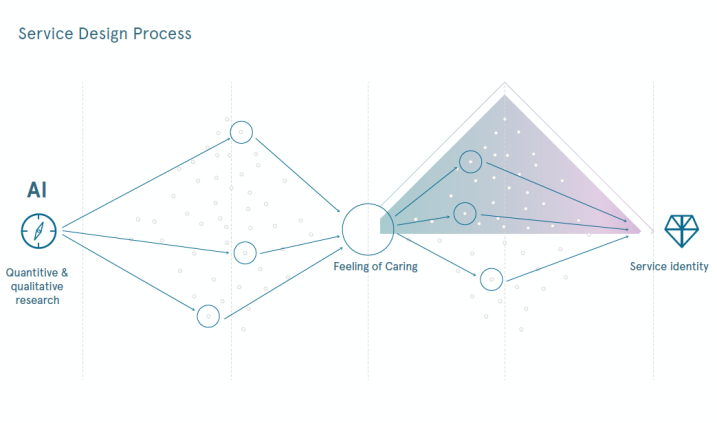
The evidence of Design 2.0 describes a collaboration between a European service design agency and a Nordic life insurance company. Machine learning models predicted that feeling of caring will have the most significant impact on customer satisfaction, customer loyalty and NPS (Net Promoter Score) of the life insurance company.
Client scoring data was totally anonymous which meant neither the client or AI could identify a customer.
After AI had forecasted that the focus of the design should be in implementing feeling of caring, a group of service and business designers could start work towards putting this into practice.
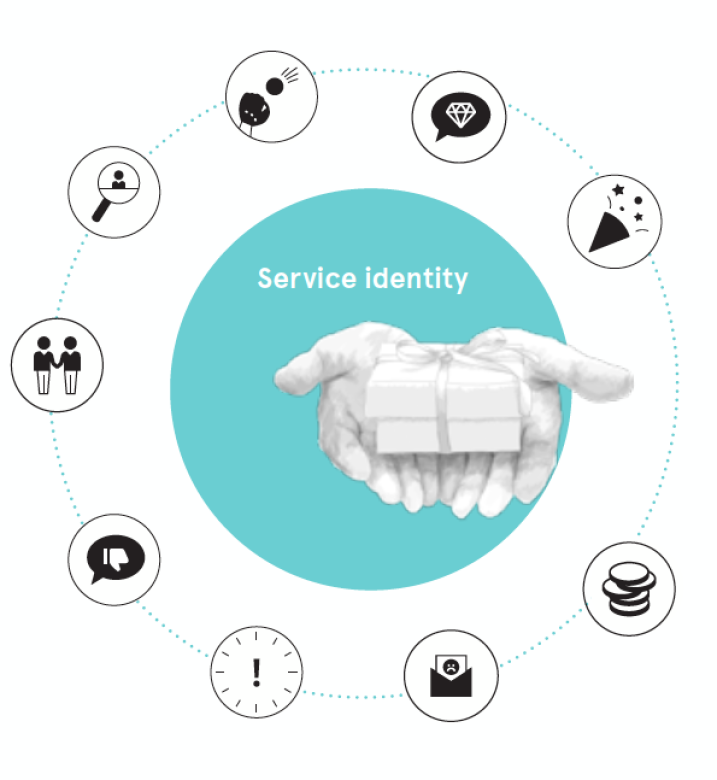
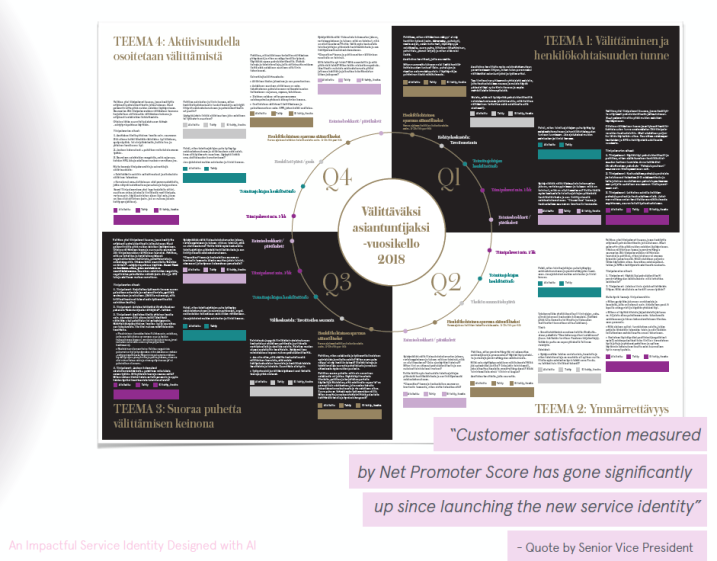
They utilized an iterative and agile double-diamond process for concretizing the feeling into service actions and co-designed a new service identity together with management and employees. The service identity took into consideration the multichannel environment (digital - physical - social) in which the life insurance company operates and serves its clients. Finally, the new service identity was translated into an effective tool and guidebook that put the “feeling of caring” into
practice across the whole organization.











Share your thoughts
0 RepliesPlease login to comment